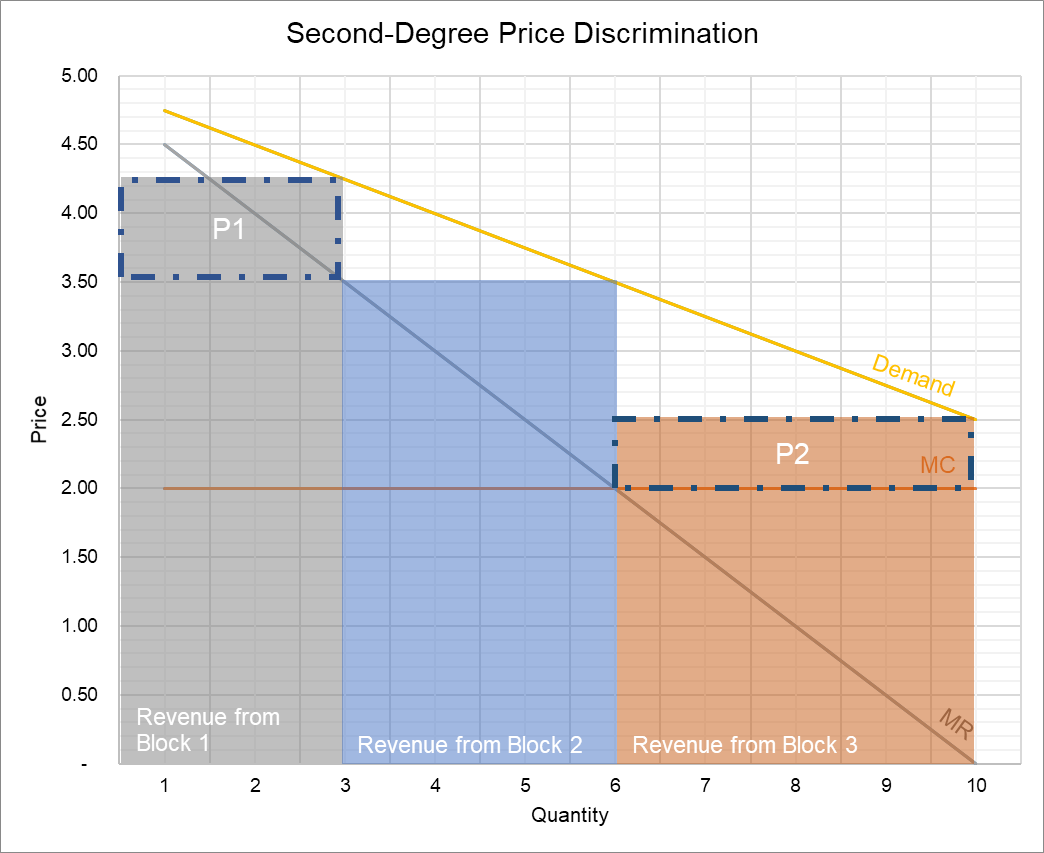
Price Discrimination Definition
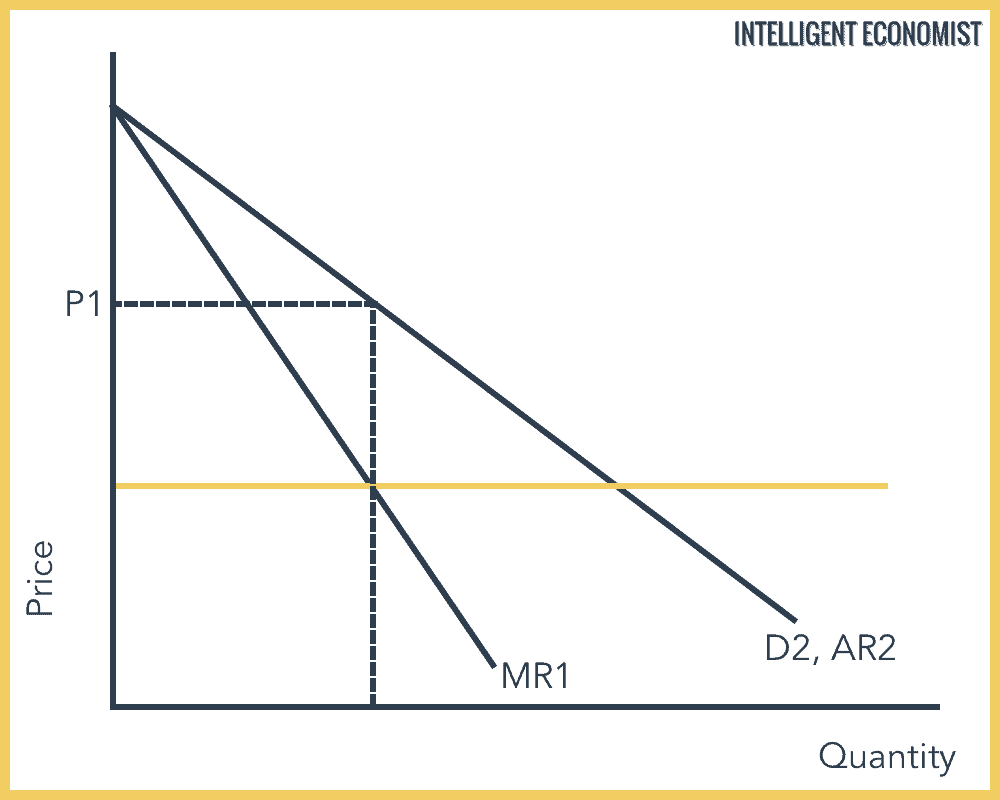
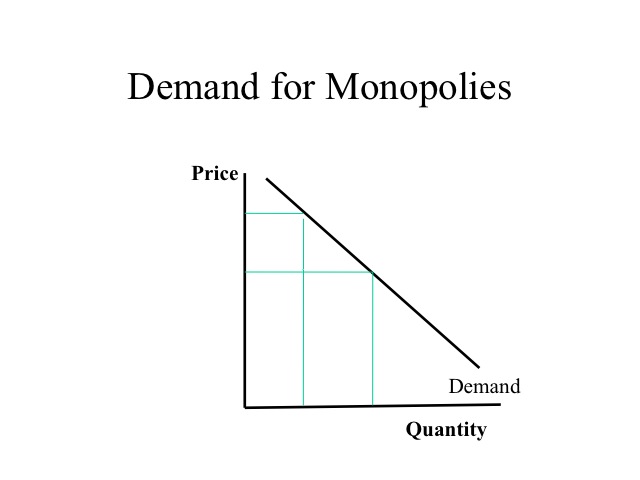
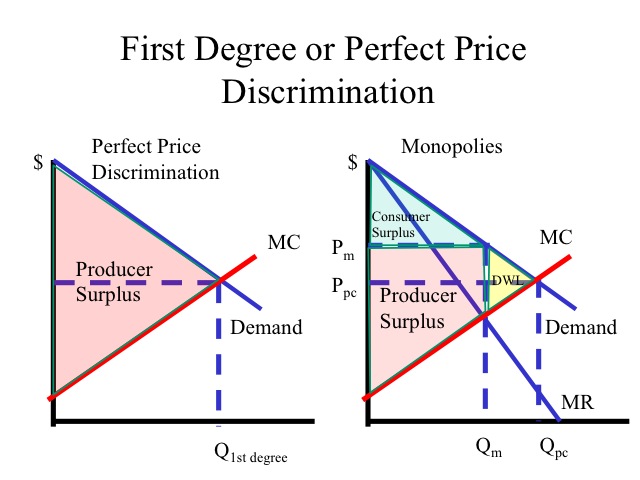
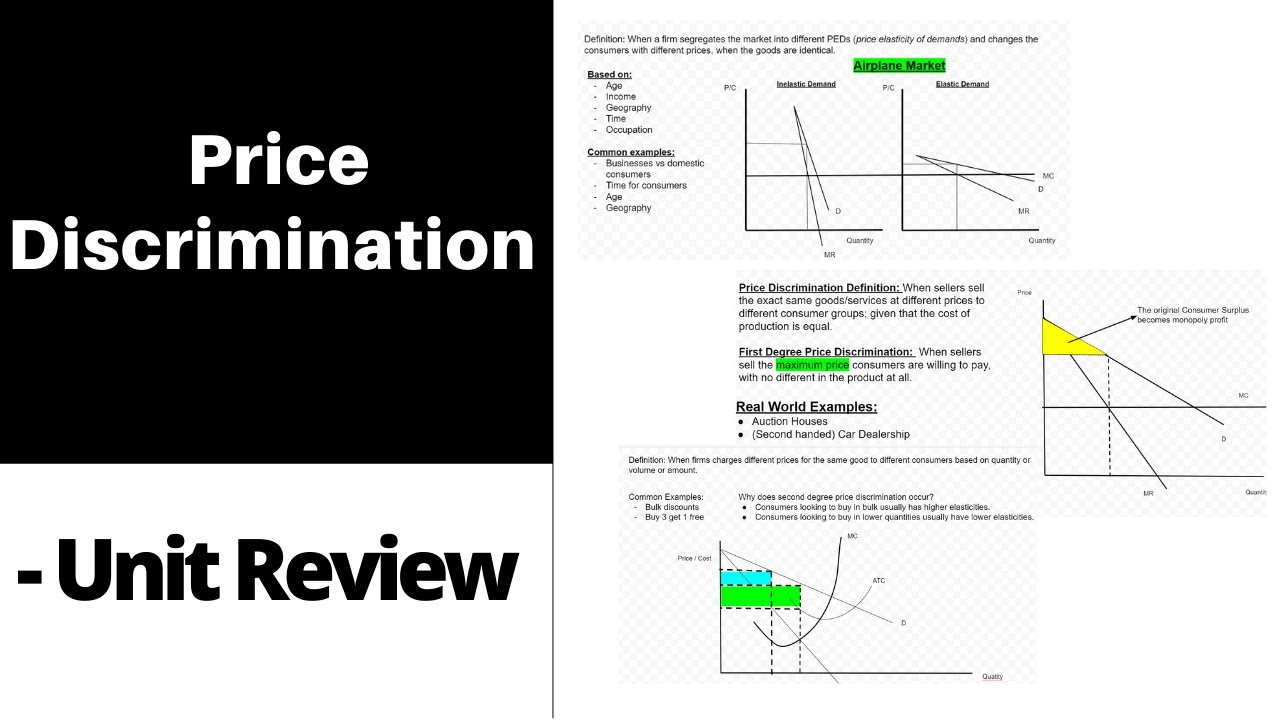
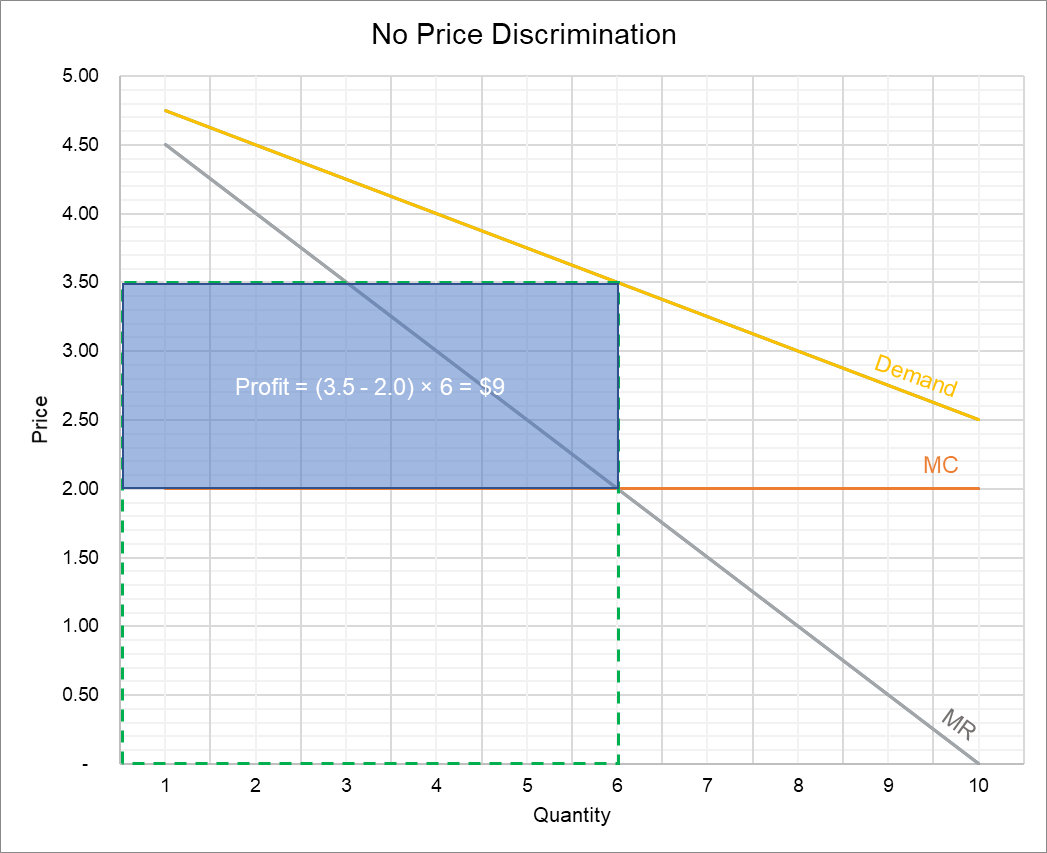
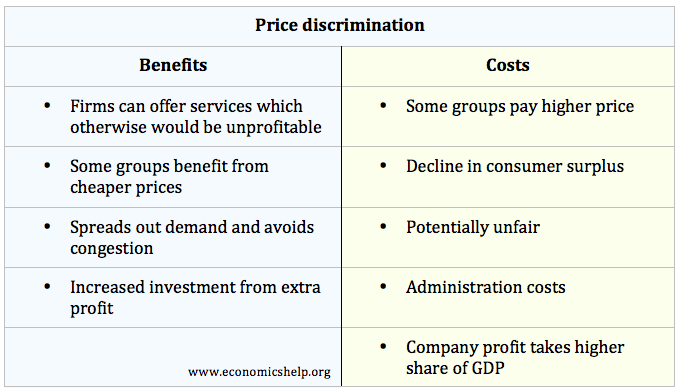
The setting of a price differential on similar goods that is not based on differences in the cost of production.
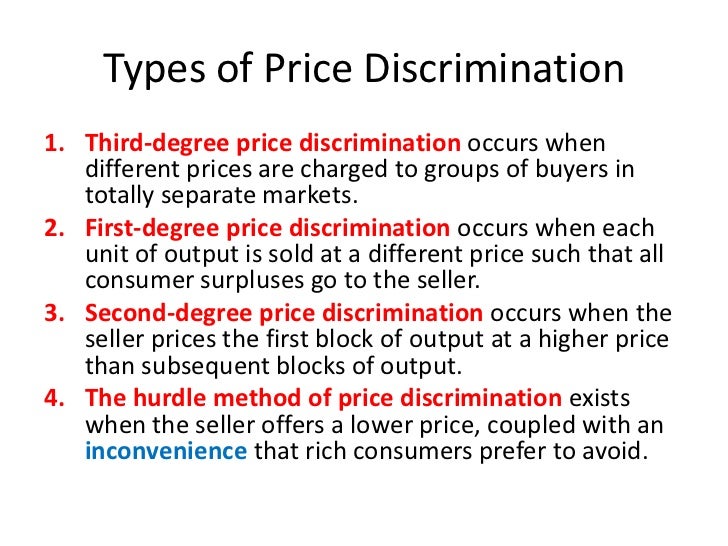
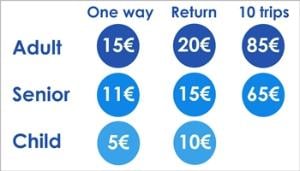
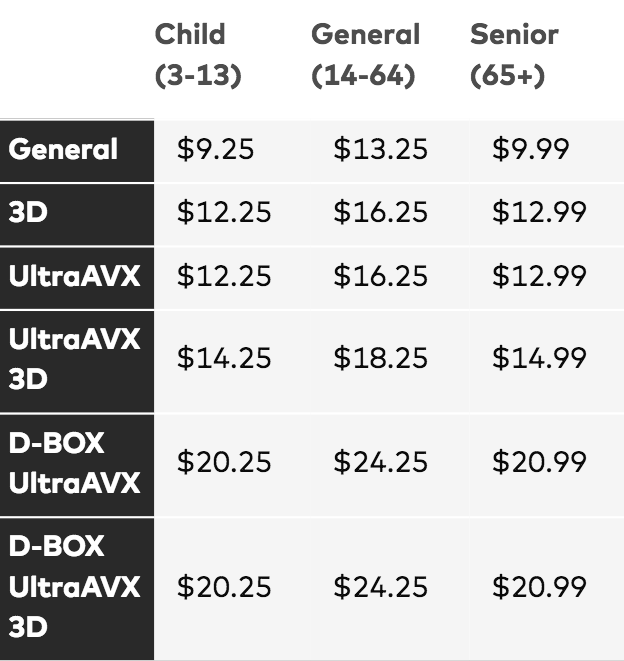
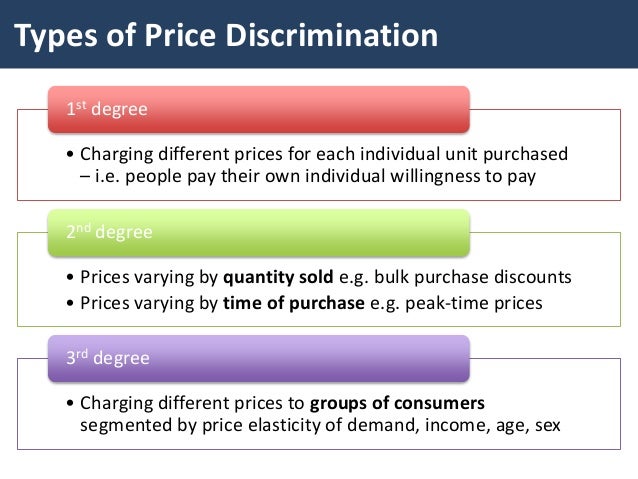
Price discrimination definition. It is a microeconomic pricing strategy where the pricing mechanism depends upon the monopoly of the company preferences of the customers uniqueness of the product and the willingness of the people to pay differently. Definition of price discrimination. The offering of similar or identical goods at different prices to different buyers. Price discrimination is a selling strategy that charges customers different prices for the same product or service based on what the seller thinks they can get the customer to agree to.
Price discrimination can be defined as a pricing strategy that is used by sellers to sell identical goods and services at different prices to a diverse group of customers based on various conditions such as demand of the product the willingness of customers to pay. Price discrimination is a pricing policy where companies charge each customer different prices for the same goods or services based on how much the customer is willing and able to pay.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-948408372-bbaef8cb64e74b92b643bf2b6150c123.jpg)